Investing in Mutual Funds: A Guide to Choosing the Right Funds

Investing in mutual funds involves selecting the right fund based on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon, requiring careful consideration of factors such as expense ratios, fund performance, and asset allocation.
Embarking on the journey of investing in mutual funds can feel like navigating a complex maze. However, with the right knowledge and a strategic approach, it can be a powerful tool for achieving your financial goals. This guide will help you choose the right funds for your investment goals.
Understanding Mutual Funds: The Basics
Before diving into the selection process, it’s vital to grasp the fundamentals of mutual funds. What exactly are they, and why are they a popular investment option?
Mutual funds essentially pool money from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of assets. This portfolio is managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions based on the fund’s stated objectives. By investing in a mutual fund, you gain access to a range of securities without having to individually research and buy them.
Benefits of Investing in Mutual Funds
Mutual funds offer several advantages for investors, particularly those who are new to the market or lack the time and expertise to manage their own investments.
- Diversification: Mutual funds provide instant diversification, reducing the risk associated with investing in individual stocks or bonds.
- Professional Management: Experienced fund managers handle the investment decisions, potentially leading to better returns.
- Accessibility: Mutual funds are relatively easy to buy and sell, with low minimum investment amounts in many cases.
Different Types of Mutual Funds
Various types of mutual funds cater to different investment goals and risk tolerances. Understanding these variations is crucial for making informed decisions.
- Equity Funds: Primarily invest in stocks, offering higher growth potential but also higher risk.
- Bond Funds: Focus on bonds, providing more stable income but lower growth prospects.
- Balanced Funds: Hold a mix of stocks and bonds, aiming for a balance between growth and income.
- Money Market Funds: Invest in short-term debt securities, offering high liquidity and low risk.

Understanding these basic differences will help you narrow down your choices as you begin evaluating specific funds.
Defining Your Investment Goals
The first step in choosing the right mutual fund is to clearly define your investment goals. What are you hoping to achieve with your investments, and what is your time horizon?
Your investment goals will significantly influence the type of mutual fund you choose. Are you saving for retirement, a down payment on a house, or your children’s education? Each goal requires a different approach and level of risk tolerance.
Determining Your Time Horizon
Your time horizon, or the length of time you plan to invest, is another critical factor to consider. Longer time horizons generally allow for more aggressive investment strategies, while shorter time horizons may require a more conservative approach.
If you have a long time horizon, such as 20 years or more, you may be comfortable with higher-risk investments like equity funds, which have the potential for higher returns over the long term. Conversely, if you have a short time horizon, such as 5 years or less, you may want to focus on lower-risk investments like bond funds or money market funds.
Assessing Your Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance refers to your ability and willingness to withstand fluctuations in the value of your investments. It’s crucial to understand your risk tolerance before selecting a mutual fund.
If you are comfortable with the possibility of losing money in exchange for the potential for higher returns, you have a high-risk tolerance. If you prefer to preserve your capital and are less concerned about maximizing returns, you have a low-risk tolerance.
By understanding your investment goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance, you can narrow down your choices and focus on mutual funds that align with your specific needs.
Evaluating Mutual Fund Performance
Once you have a clear understanding of your investment goals, you can begin evaluating the performance of different mutual funds. This involves analyzing various metrics to assess how well a fund has performed in the past and how it is likely to perform in the future.
Past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results, but it can provide valuable insights into a fund’s investment strategy and its ability to generate returns over time.
Key Performance Metrics to Consider
Several key performance metrics can help you evaluate mutual funds effectively.
- Returns: Look at both short-term (1-year) and long-term (3-year, 5-year, 10-year) returns to assess a fund’s performance over different time periods.
- Expense Ratio: This is the annual fee charged by the fund to cover its operating expenses. Lower expense ratios generally lead to higher returns for investors.
- Turnover Rate: This measures how frequently the fund manager buys and sells securities within the portfolio. Higher turnover rates can result in higher transaction costs and potentially lower returns.
Comparing Funds Within the Same Category
When evaluating mutual fund performance, it’s important to compare funds within the same category. This will give you a more accurate picture of how a fund is performing relative to its peers.
For example, if you are considering investing in an equity fund, compare its performance to other equity funds with similar investment objectives. This will help you identify funds that have consistently outperformed their peers over time.
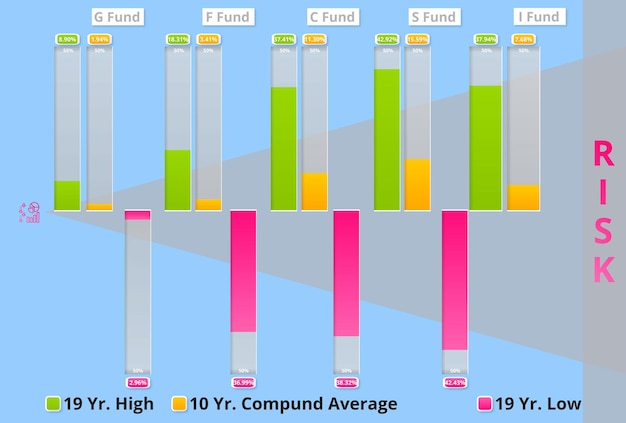
By carefully evaluating these performance metrics and comparing funds within the same category, you can make more informed investment decisions.
Understanding Fund Fees and Expenses
Fund fees and expenses can significantly impact your investment returns. It’s crucial to understand these costs and their potential impact before investing in a mutual fund.
Even seemingly small fees can erode your returns over time, so it’s essential to choose funds with low expense ratios and avoid funds with hidden fees.
Types of Fees and Expenses
Various types of fees and expenses are associated with mutual funds.
- Expense Ratio: As mentioned earlier, this is the annual fee charged by the fund to cover its operating expenses.
- Sales Load: This is a commission charged when you buy or sell shares of the fund. Some funds have front-end loads, which are charged when you buy shares, while others have back-end loads, which are charged when you sell shares.
- Management Fee: This is the fee paid to the fund manager for managing the fund’s investments. It is typically a percentage of the fund’s assets under management.
The Impact of Fees on Returns
Fees can have a significant impact on your investment returns over time.
For example, if you invest $10,000 in a mutual fund with an expense ratio of 1%, you will pay $100 in fees each year. Over 20 years, these fees can add up to thousands of dollars, significantly reducing your overall returns.
Therefore, it’s important to choose funds with low expense ratios and avoid funds with unnecessary fees. Consider investing in no-load funds, which do not charge sales commissions.
By understanding the various fees and expenses associated with mutual funds, you can make more cost-effective investment decisions.
Choosing the Right Fund Type for Your Needs
With a solid understanding of mutual fund basics, investment goals, and evaluation metrics, the next step is to select the right type of fund that aligns with your specific needs.
This involves considering your risk tolerance, time horizon, and investment objectives to determine whether an equity fund, bond fund, balanced fund, or another type of fund is the best fit.
Equity Funds: Growth Potential
Equity funds, which primarily invest in stocks, offer the potential for high growth but also come with higher risk. These funds are typically suitable for investors with a long time horizon and a high-risk tolerance.
Different types of equity funds cater to various investment styles, such as growth funds, value funds, and dividend funds. Growth funds focus on companies with high growth potential, while value funds focus on undervalued companies. Dividend funds focus on companies that pay regular dividends.
Bond Funds: Income and Stability
Bond funds, which primarily invest in bonds, offer more stable income but lower growth prospects. These funds are typically suitable for investors with a shorter time horizon and a low-risk tolerance.
Different types of bond funds cater to various maturity lengths and credit qualities. Short-term bond funds invest in bonds with shorter maturities, while long-term bond funds invest in bonds with longer maturities. High-quality bond funds invest in bonds with high credit ratings, while low-quality bond funds invest in bonds with low credit ratings.
By matching your investment needs with the appropriate fund type, you can optimize your portfolio for your specific circumstances.
Building a Diversified Portfolio
Diversification is a key principle of successful investing. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, you can reduce your overall risk and potentially improve your returns.
Mutual funds make diversification easy, but it’s still important to ensure that your portfolio is well-diversified across different sectors, industries, and geographic regions.
Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation refers to the process of dividing your investments among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash. The optimal asset allocation strategy depends on your investment goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance.
A common asset allocation strategy is the 60/40 portfolio, which consists of 60% stocks and 40% bonds. This strategy aims to provide a balance between growth and income. However, you may need to adjust this allocation based on your individual circumstances.
Rebalancing Your Portfolio
Over time, your asset allocation may drift away from your target allocation due to market fluctuations. It’s important to rebalance your portfolio periodically to bring it back into alignment with your target allocation.
Rebalancing involves selling some of your investments that have performed well and buying more of your investments that have underperformed. This can help you maintain your desired level of risk and potentially improve your returns over the long term.
Effective diversification and regular rebalancing are essential for building a resilient and successful investment portfolio.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🎯 Define Goals | Clearly outline your investment objectives. |
| ⚖️ Assess Risk | Understand your comfort level with potential losses. |
| 💰 Check Fees | Consider expense ratios and other costs. |
| diversificate Portfolio | Spread investments across different asset classes. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle that pools money from many investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets, managed by a professional fund manager.
▼
Consider your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Evaluate past performance, fees, and the fund’s investment strategy before making a decision.
▼
Expense ratios are annual fees charged by the fund to cover operating expenses, including management fees and administrative costs. Lower expense ratios can lead to higher returns.
▼
Diversification is a strategy of spreading your investments across different asset classes to reduce risk. Mutual funds provide instant diversification by holding a variety of securities.
▼
Rebalancing should be done periodically, typically once a year or whenever your asset allocation drifts significantly from your target allocation. This ensures your portfolio aligns with your risk tolerance.
Conclusion
Investing in mutual funds can be a powerful way to achieve your financial goals. By understanding the basics, defining your objectives, evaluating performance, and building a diversified portfolio, you can make informed decisions and maximize your chances of success.